5.2 Joins
We mentioned earlier that there are several kinds of ways we can join data. The different kinds of joins are described below.
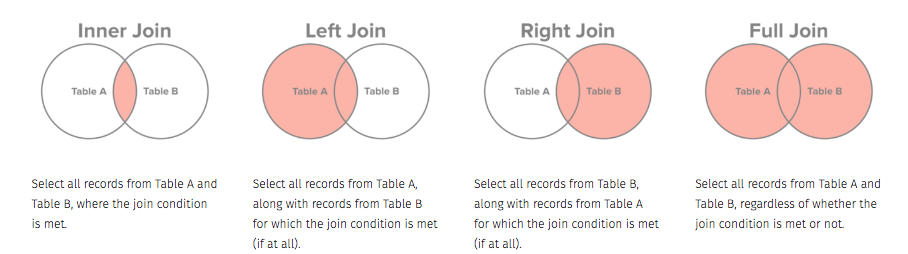
Let’s look at these joins with an example. We have two simulated datasets looking at DOS real estate allocation and staffing. We will look at how much area on average each bureau has given the number of employees
staffing_data <- import('data/Staffing_by_Bureau.csv') %>% as_tibble()
real_estate <- import('data/DoS_Real_Estate_Allocation.csv') %>% as_tibble()
real_estate## # A tibble: 666 x 4
## Building Bureau Location Size
## <chr> <chr> <int> <int>
## 1 HST Administration (A) 4779 640
## 2 SA2 Administration (A) 4801 1090
## 3 HST Administration (A) 5109 1040
## 4 HST Administration (A) 3717 1620
## 5 SA4 Administration (A) 3940 1390
## 6 HST Administration (A) 3661 1480
## 7 HST Administration (A) 3374 1770
## 8 HST Administration (A) 3387 1940
## 9 SA10 African Affairs (AF) 2605 640
## 10 HST African Affairs (AF) 3573 720
## # … with 656 more rowsstaffing_data## # A tibble: 10,000 x 6
## Bureau Gender Grade Title Name YearsService
## <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <int>
## 1 Protocol (S/CPR) female FS1 Manager Cathy Ca… 13
## 2 Administration (A) male GS-9 Team Me… Jeffery … 13
## 3 Intelligence and Research … male FS-6 Analyst Max Green 11
## 4 Mission to the United Nati… male FS-3 Manager Donald A… 7
## 5 Foreign Missions (OFM) male FS-6 Team Me… Thomas L… 22
## 6 International Narcotics an… male GS-8 Team Me… Joseph A… 12
## 7 Administration (A) male GS-12 Analyst Michael … 6
## 8 Intelligence and Research … male FS-5 Team Me… Jesus Sh… 2
## 9 Science & Technology Advis… male N/A Manager Lawrence… 19
## 10 Administration (A) female FS-8 Team Me… Jennie C… 17
## # … with 9,990 more rowsThe strategy is going to be to do a grouped summary of the staffing data to see how many people are in each Bureau, and then join that with the real estate data to compute the average area per employee by Bureau.
staff_summary <- staffing_data %>%
group_by(Bureau) %>%
tally(name = 'Pop')
realestate_summary <- real_estate %>%
group_by(Bureau) %>% summarize(Size = sum(Size))
realestate_summary %>% left_join(staff_summary) %>%
mutate(unit_area = Size/Pop) %>%
arrange(unit_area)## Joining, by = "Bureau"## # A tibble: 54 x 4
## Bureau Size Pop unit_area
## <chr> <int> <int> <dbl>
## 1 Global Youth Issues (GYI) 2090 345 6.06
## 2 Policy Planning Staff (S/P) 2420 240 10.1
## 3 Science & Technology Adviser (STAS) 4240 305 13.9
## 4 Foreign Missions (OFM) 4420 311 14.2
## 5 Trafficking in Persons (TIP) 5150 247 20.9
## 6 Medical Services (MED) 6760 308 21.9
## 7 Protocol (S/CPR) 7730 327 23.6
## 8 Administration (A) 10970 454 24.2
## 9 Oceans and International Environmental and Scient… 8420 330 25.5
## 10 Energy Resources (ENR) 10890 369 29.5
## # … with 44 more rows